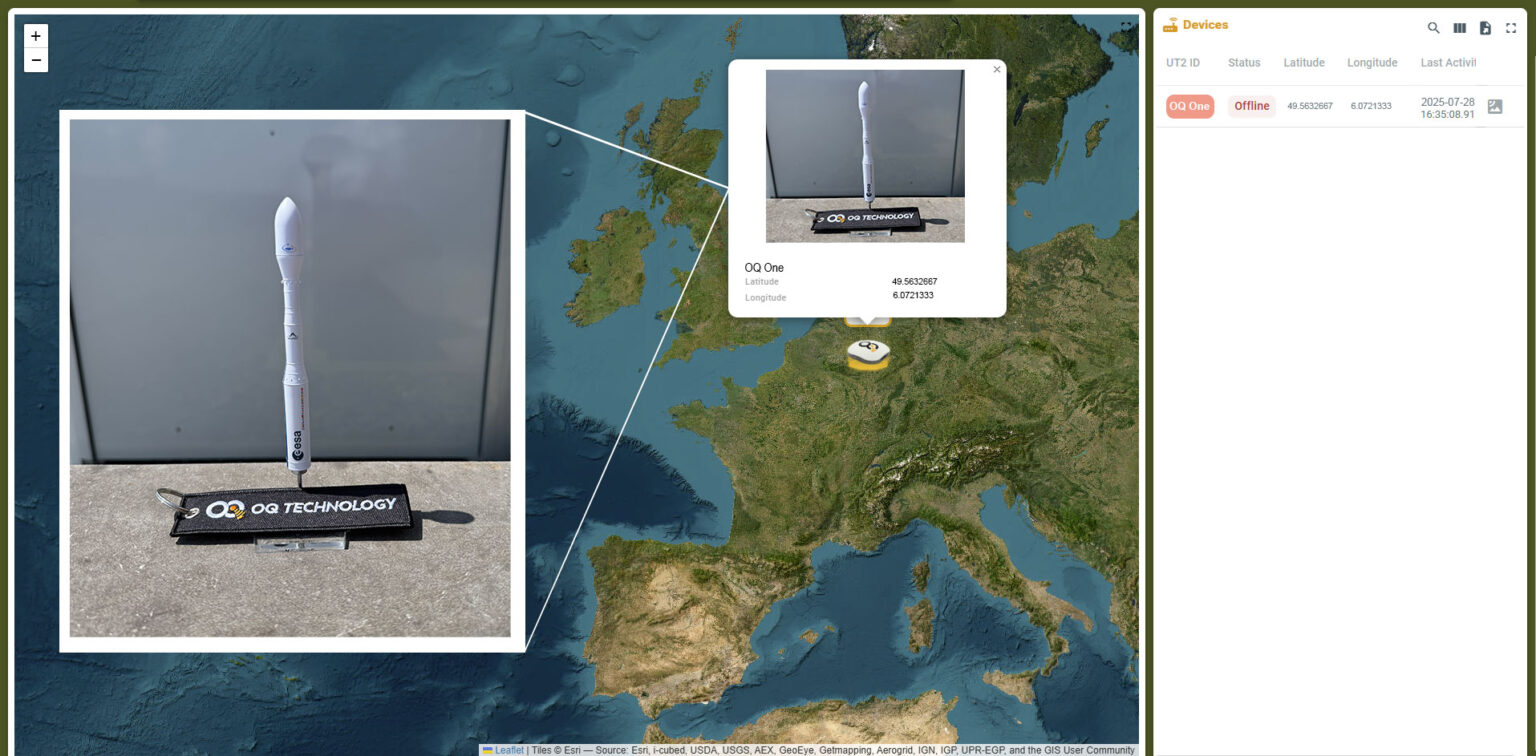
In a major breakthrough for satellite-based Internet of Things (IoT), Luxembourg-based OQ Technology has achieved a world-first by transmitting an image via its 5G non-terrestrial network (NTN) over a low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite, using the S-band spectrum and 3GPP-standardized 5G IoT protocols.
The successful demo marks a pivotal moment for remote visual monitoring, enabling real-time image transmission from areas far beyond the reach of terrestrial networks.
Turning visual IoT into reality
The demonstration involved a motion-triggered camera linked to OQ’s proprietary 5G NTN terminal (OQ ONE). Upon activation, it captured an image of a model rocket and sent it via OQ’s LEO satellite constellation to a nearby ground station—entirely bypassing conventional network infrastructure.
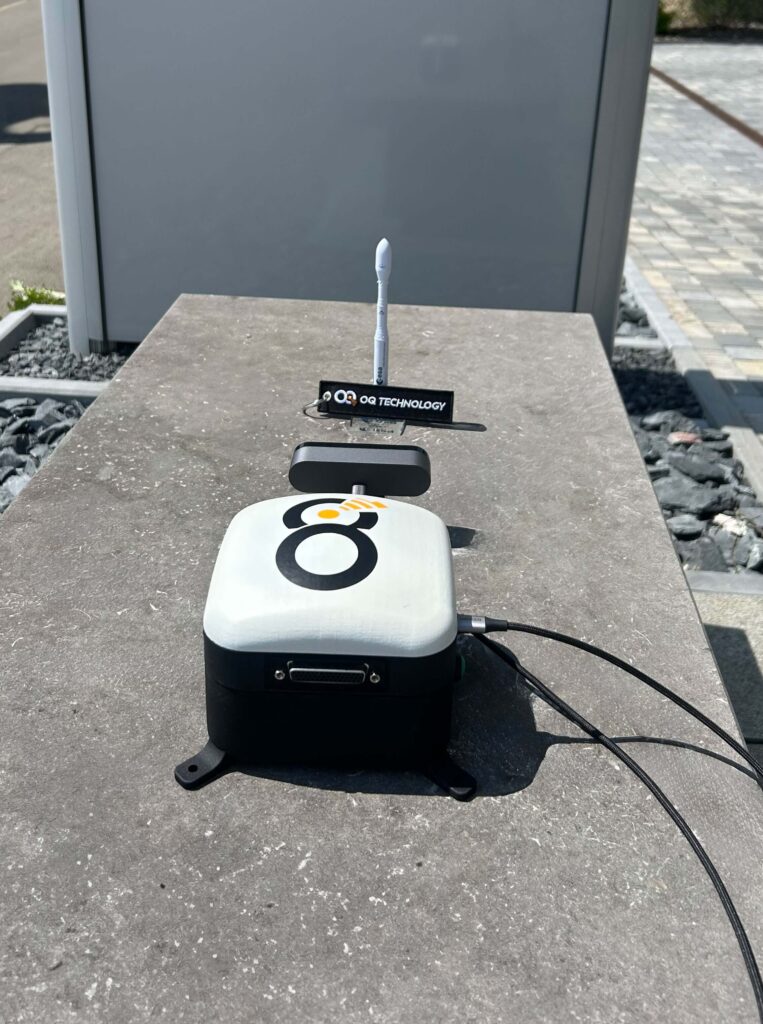

“Being able to send images over satellite makes our 5G network dramatically more powerful,” said Omar Qaise, Founder & CEO of OQ Technology. “Whether it’s an oil rig, power station, or environmental sensor in the middle of nowhere, you can now see what’s happening, not just measure it.”
Expanding use cases for satellite IoT
The new capability is set to unlock visual data applications across several high-impact industries:
- Energy & utilities: Image-based monitoring of remote pipelines, solar farms, and substations
- Defense & security: Real-time visual feeds from border sensors, drones, and mobile surveillance units
- Agriculture: Remote imagery for crop and livestock monitoring
- Disaster response: Fast visual assessment of affected zones to guide relief efforts
- Industrial maintenance: Visual confirmation of automated alerts and system faults
With this added visual capability, OQ’s low-latency, high-resilience 5G NTN IoT network becomes an even more compelling solution for mission-critical operations in isolated environments.
A preview of next-gen IoT
Far beyond a proof-of-concept, the milestone sets the foundation for a new era in satellite IoT—one where machines not only send data but also share what they see. OQ Technology continues to push toward scalable deployment of visual IoT services across its expanding satellite constellation.